
For example, the direct labor necessary to produce a wood desk might include the wages paid to the assembly line workers. Indirect labor is labor used in the production process that is not easily and economically traced to a particular product. Examples of indirect labor include wages paid to the production supervisor or quality control team.
Direct labor efficiency variance
As demonstrated in this chapter, standard costs and variance analysis are tools used to project manufacturing product costs and evaluate production performance. Standard costs variance analysis is used to determine the variances between the standard amounts projected for manufacturing costs and the actual amounts incurred. Any variance between the standard amounts allowed and actual amounts incurred should be investigated.
What is a variance analysis?
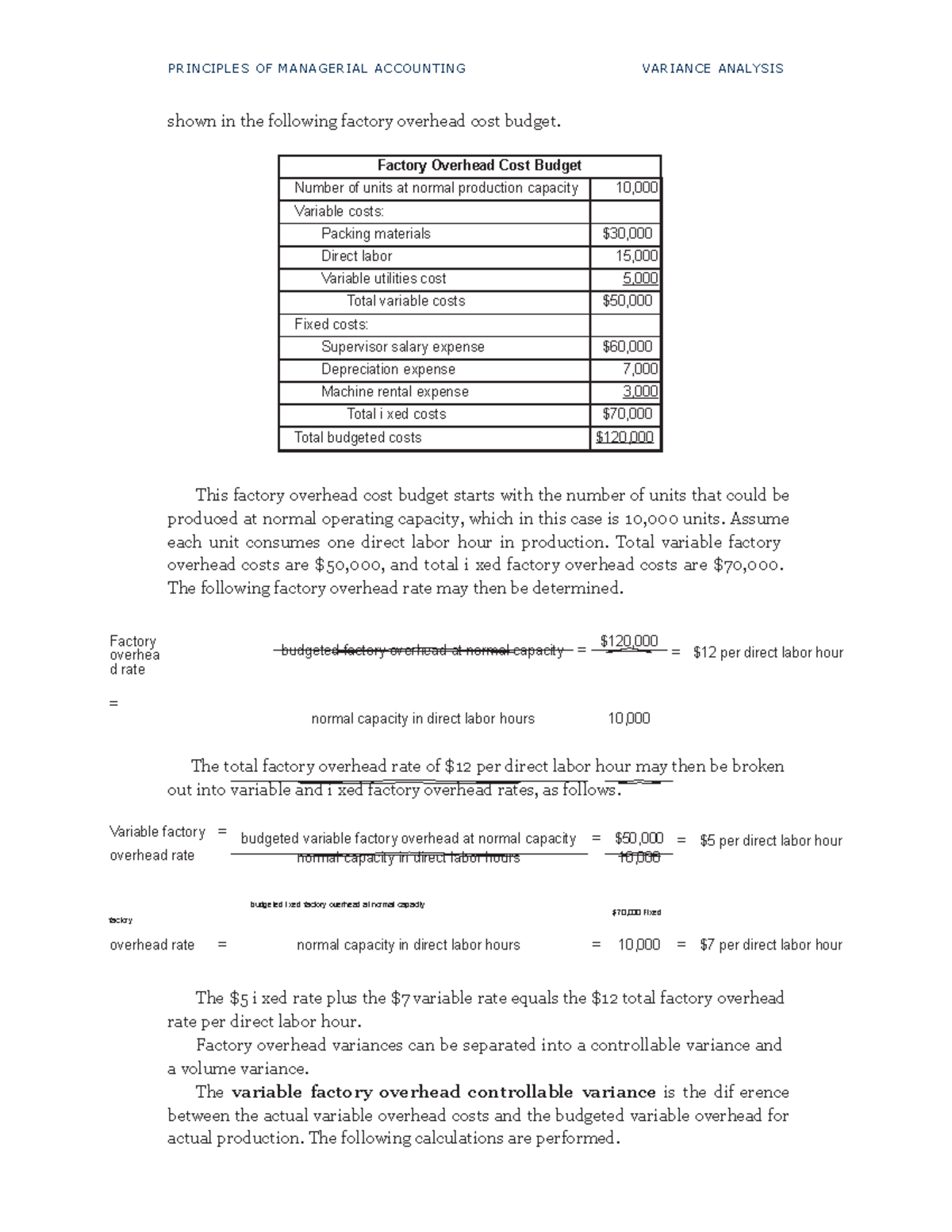
Sales volume variance accounts for the difference between budgeted profit and the profit under a flexed budget. All remaining variances are calculated as the difference between actual results and the flexed budget. The factory overhead cost budget is prepared a bit differently, listing a dollar amount for each cost. Some factory subject to change 2021 overhead costs may be further broken out into their fixed and variable components. Suppose Connie’s Candy budgets capacity of production at \(100\%\) and determines expected overhead at this capacity. Connie’s Candy also wants to understand what overhead cost outcomes will be at \(90\%\) capacity and \(110\%\) capacity.
Variance Analysis: Practical Questions and Answers
As with direct material and direct labor, it is possible that the prices paid for underlying components deviated from expectations (a variable overhead spending variance). On the other hand, it is possible that the company’s productive efficiency drove the variances (a variable overhead efficiency variance). Thus, the Total Variable Overhead Variance can be divided into a Variable Overhead Spending Variance and a Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance. Since direct labor hours are the cost driver for variable manufacturing overhead in this example, the variance is linked to the direct labor hours worked in excess of the standard labor hours allowed.
Total variable manufacturing costs variance
Fixed overhead, however, includes a volume variance and a budget variance. Connie’s Candy used fewer direct labor hours and less variable overhead to produce \(1,000\) candy boxes (units). Usually, the level of activity is either direct labor hours or direct labor cost, but it could be machine hours or units of production.
But after breaking down the variances, you notice that your revenue is greater than predicted, but you spent more on materials than anticipated. Using this information, you can shop around for new vendors and cut down unnecessary expenses. You can measure your total variance (e.g., your budget as a whole) or break it down (e.g., sales revenue). Finding specific variances can give you a more detailed view of your business’s performance and financial health. Only looking at your total variance could give you a skewed impression of your business’s performance and health.
- The actual quantity purchased and used to produce 150,000 units was 600,000 feet of flat nylon cord costing $330,000.
- During the period, Brad projected he should pay $112,500 for variable manufacturing overhead to produce 150,000 units.
- Actual cost of production may be different than standard cost if any of the five goals listed above is either not met or exceeded.
- Total variable manufacturing overhead costs per the standard amounts allowed are calculated as the total standard quantity of 37,500 times the standard rate per hour of $3 equals $112,500.
Sure, it’s great that you’re doing better in said area than you predicted. But by assessing the reason why, you may be able to apply that success to underperforming areas. Follow these general steps to start your variance analysis in cost accounting. You can conduct a variance analysis of financial statements, hours your employees log, purchase receipts, etc. Due to the different types of variances, you might measure variances in dollars, units, or hours. Favorable variances mean you’re doing better in an area of your business than anticipated.
The standard cost of the expected materials and the actual cost of the materials used can be compared to determine material variance in accounting. Price variation (variation in cost per unit) and quantity variance (variation in utilization or quantity of materials) are the two main components of material variance. Variance in accounting refers to the variation or difference between forecasted or budgeted amounts and the actual amounts incurred or achieved. It is commonly used to compare predictions and real outcomes across business operations. Favorable variances indicate better-than-expected performance, while unfavorable variances indicate a shortfall compared to expectations.
A cost driver, typically the production units, drives the variable component of manufacturing overhead. As with any variable cost, the per unit cost is constant, but the total cost depends on the quantity produced or another cost driver. The focus of this section is variable manufacturing overhead since it has both a quantity and price standard. The total price per unit variance is the standard price per unit of $0.50 less the actual price paid of $0.55 equals the price variance per unit of $(0.05) U. This is unfavorable because they actually spent more per unit than the standards allowed. The fixed factory overhead variance represents the difference between the actual fixed overhead and the applied fixed overhead.
It is similar to the labor format because the variable overhead is applied based on labor hours in this example. For example, if the actual cost is lower than the standard cost for raw materials, assuming the same volume of materials, it would lead to a favorable price variance (i.e., cost savings). However, if the standard quantity was 10,000 pieces of material and 15,000 pieces were required in production, this would be an unfavorable quantity variance because more materials were used than anticipated. Standard cost projections are established for the variable and fixed components of manufacturing overhead. Manufacturing overhead includes all costs incurred to manufacture a product that are not direct material or direct labor. The completed top section of the template contains all the numbers needed to compute the direct labor efficiency (quantity) and direct labor rate (price) variances.

Leave a Reply